Blockchain and AI are both equally buzzwordy terms in the marketplace of ideas, especially when it comes to turning either one scalable. Recently, however, efforts have been made to consolidate both, making blockchain more efficient with even less human involvement. You might think, “What is blockchain, and why should I care about it?”
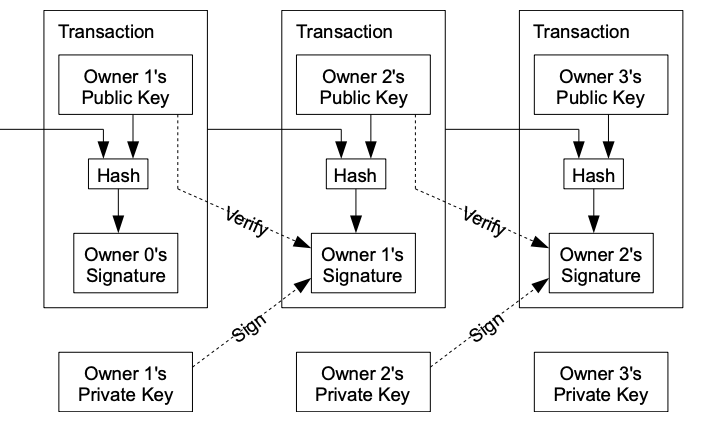
In layman’s terms, blockchain is a private digital transaction logger that can be shared with multiple parties. Blockchain is unique because it can log many different types of assets, from concrete objects such as houses, cars, etc., to intellectual property or a picture with a specific hash that gives it value (NFTs).
What makes blockchain important, especially large-scale, is the speed and efficiency with which it transfers information between many different authorized parties. When each buy or sale of an asset adds on to another, it creates a ledger (literally, a chain of blocks) which helps further verify legitimate blockchains and make the system functionally tamper-proof.
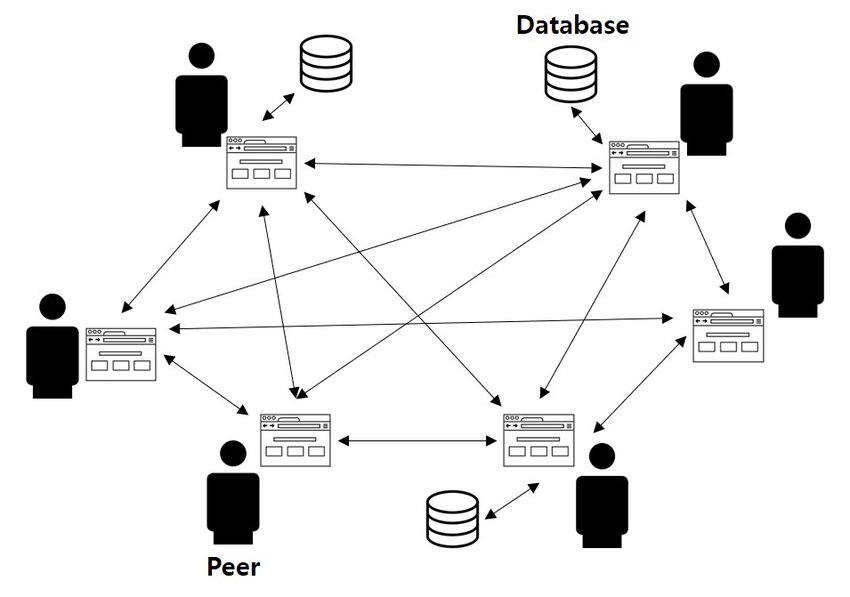
So how does artificial intelligence fit into this larger matrix?
First, let’s start with the benefits blockchain brings to AI. The most obvious one is being able to run machine learning models on less powerful machines, an option not possible with current AI infrastructure. Blockchain on a mobile device, for example, would enable cheaper and easier access to data sets, a crucial resource for startups to get off the ground faster. Blockchain’s security measures also help provide a layer of transparency to the AI black box; It creates a method to trace back and regulate AI exposure to ensure that an AI-powered blockchain works both ethically and expeditiously.
Blockchain isn’t carrying all the weight in this technological marriage, however. AI can make mining cryptocurrency more efficient by doing the required calculations faster, allowing the blockchain system to run faster and helping crypto sustainability efforts by reducing carbon emissions writ large. AI can also be utilized to make more efficient security measures for blockchain, such as dedicated security algorithms that can detect false blocks with far more breadth and depth than a human ever could. Even in trading crypto, AI can make far more educated decisions that consider the market’s volatility at any given moment. There are copious applications for AI in the blockchain, which some projects, such as FutureFi and SingularityNET, have already begun to take advantage of. Projects such as these have enabled producers to sell AI-driven data, services, and algorithms to a far broader base than previously imagined.
Regardless of where these systems progress into the 21st century, one thing is clear: both these areas of study will continue growing closer together, and it’s up to the consumer to either embrace the change or stick to the ways of the old market. Undoubtedly, AI-powered blockchains are the future of human networking and transactions.